Table of Contents
After Reading This Guide, You’ll Understand 🡭
- How to evaluate the ranking opportunity of a keyword
- How to prioritize your keyword list
Concepts To Know Before Reading This Guide 🡭
Ranking difficulty – The ranking difficulty is a concept of identifying the ranking difficulty of your website for the target keyword.
Keyword difficulty (KD) – “KD is calculated using our own unique algorithm, and it is based on the number of referring domains (RDs) the Top 10 ranking pages (organic search results only) for a given keyword have.” – Ahrefs.
Why It Is Important To Measure The Ranking Difficulty of Keywords 🡭
Many websites write and publish a ton of content, but they hardly get organic traffic due to many reasons.
One of the key reasons for not ranking your web pages on the first page is targeting keywords with higher ranking difficulty.
An ineffective approach to keyword research and content creation looks like this:
- Make a list of seed keywords (broad keywords) related to your niche
- Add these keywords to any SEO tool (like ahrefs, Semrush) and get long-tail keywords
- Filter the keyword list with keyword difficulty
- Now, create content for these keywords with low KD
The biggest fault in this approach is that while selecting the right keywords, you focus solely on KD and ignore other important metrics such as search intent, topical authority, relevance gap, etc.
Better approach?
Not taking your SEO decision only because of low keyword difficulty. And also considering other metrics to choose the right keywords.
Here is a 4 point checklist that I use every time to evaluate the ranking opportunity:
1. Backlink profile 🡭
Ranking on the first page isn’t just about having more backlinks. But still, it helps to a great extent.
Auditing backlink profiles of the top 10 pages are a good starting point.
Here’s an example of analyzing top pages with Ahrefs:
When analyzing backlink strength, you need to look at the quantity and quality of backlinks on the top pages.
Let me give you an example:
One of the top pages for the search term ‘corporate gifts for employees’ is a webpage from Igp.com.
Now, when you look at the backlink profile, you’ll see that the page has 900+ backlinks from 100+ different domains.
This seems like a very strong backlink profile and hard to beat for any new website. But I recommend studying the quality of these backlinks as well.
When you look at the individual backlinks, you’ll find that most of the backlinks are from coupon sites, irrelevant search filters, etc.
In fact, some of these irrelevant links have high domain ratings of 50+. In reality, these types of links are not going to help you win in SEO.
Now, you can understand the major problems of relying only on the keyword difficulty (KD) metric shown in different SEO tools.
Even if the top pages have 500+ backlinks from 100+ referring domains, you should dive deep to manually study the quality of these backlinks because domain rating and backlinks can be manipulated easily.
This way, you can truly understand the actual backlink strength of top pages.
2. Content depth 🡭
The second thing you need to check is the content depth of the top pages. Content depth refers to how well the articles have covered the topic.
Now, many SEO tools will give you the average word count of the top pages. But evaluating content depth by looking at the average word count of the top 10 pages is really a bad idea.
Instead, you should be doing one of the following:
- Manual check
- Look at the heading structure of these pages
- Take help from SEO tools (Frase, MarketMuse, etc.) to know the list of topics and entities covered on the top pages.
Sharing content structure of two web pages with different content depth.
Here’s page 1:
Here’s page 2:
You can see that the content depth of page 2 is much higher than on page 1. So, from a content depth perspective, page 2 will have a clear advantage in this case.
In short:
- Don’t just look at the average word count of top pages to evaluate content depth
- Look at the key topics, headings, and questions covered in the top-ranking pages
This way, you can find ranking opportunities when looking at the content depth.
Tools you can use:
- Thruuu (SERP analyzer) – free version available
- MarketMuse – free version available
- MarketingSyrup SEO pro – Chrome extension
3. Topical Authority 🡭
In the quality raters guideline, Google says that ‘the amount of expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness (E-A-T) of main content and the website is very important.’
This also means that becoming an expert in all topics is hardly possible for any website.
Let’s take some examples of sites and their expertise in the field:
- Investopedia → investing and financial education
- HackerNoon → technology insights and updates
- YourStory → stories and insights about startup and entrepreneurship
And, you’ll see that these websites mostly create content about their core expertise, not on all topics available on the internet.
But there are popular sites (Strong backlink profile) that lack expertise and authoritativeness in a specific niche because they publish content on all topics.
Now, this will give you a lot of opportunities to outrank top pages.
Here’s what to do:
First, type your target keyword in Google and look at the top pages.
Now, ask the following questions:
- Do these pages have topical authority on the topic?
- Do these websites publish content on various topics (say health, marketing, business, finance, etc.)?
This way, you can find the opportunity to even outrank bigger websites than yours.
A real example:
Let’s consider a target keyword: Factors affecting investment
And, when you look at the SERP, you’ll find some of the pages (yourarticlelibrary. com) lack topical authority in the finance management or economics topic.
In fact, the website (yourarticlelibrary. com) publish content on almost every topic, such as travel, environment, business, health, etc.
If you see a similar case in your SERP analysis, it should be an opportunity to beat the competitor in topical authority.
In short: There is a topical authority gap if you see most of the top pages are generic sites that do not have authority in the topic.
4. Search Intent 🡭
Search intent is about understanding the WHY behind users’ queries.
Generally, we categorize all search terms into four different search intents:
- Information
- Navigational
- Commercial
- Transactional
Understanding keyword’s search intent will help you create the most relevant webpage for the user.
To get a better idea, you need to study the SERP and understand the type of pages (service pages, blog posts, category pages, directory listing, etc.) ranking on the first page.
An example:
Let’s analyze the SERP for the search term ‘work from home furniture price.’
As you can see, most of the pages from the SERP are category pages. If you had to target this search term, it would be better to create a category page (with relevant content and product listings) instead of creating a blog post or single product page.
Take a step further:
Search intent is not just about finding whether a keyword belongs to information, transactional, or any other category.
You also need to understand the content angle by looking at the top pages.
Here’s what I mean:
If you look at the below SERP for the search term ‘content marketing audit,’ you’ll see that most of the pages are talking about a step-by-step and how-to guide.
Therefore, you’ll get the idea that users are looking for a complete step-by-step process to run a content marketing audit.
This way, you can optimize your content structure and include relevant sub-topics.
How to track search intent shifts?
Yes, search intent for a search term isn’t fixed. It is highly possible to see information articles dominating the SERP that used to be dominated by category or product pages.
This is another reason why you should always look for a content update check periodically.
Now, you can even track search intent shifts using tools like Ahrefs, SERanking, etc.
In Ahrefs, when you start the keyword research, you’ll find a feature called SERP position history that looks like this:
By looking at the charts, you’ll understand what type of pages are dominating the SERP for the target keyword.
The following guides will help you explore Ahrefs and track the search intent shift:
5. Prioritize Keywords at Scale With Google Sheet [Template]
Many keyword research processes lack the keyword prioritization step.
That means you have a huge list of keywords and start taking any random keyword and creating the content around it.
Then you select another random keyword from the list and create the content.
And, this process goes on.
The problem with this approach is that not all keywords are equal in terms of:
- Traffic potential
- Search volume
- Business value
And, you may skip the most valuable keywords unknowingly and start chasing less valuable keywords.
Better approach?
Prioritize your keyword list to make data-driven decisions about:
- Which keywords will have the most impact?
- Which keywords should I skip right now?
- Where do I begin with the keyword list?
Here’s the Google sheet that will help you prioritize and visualize the entire process (link to download is given below).
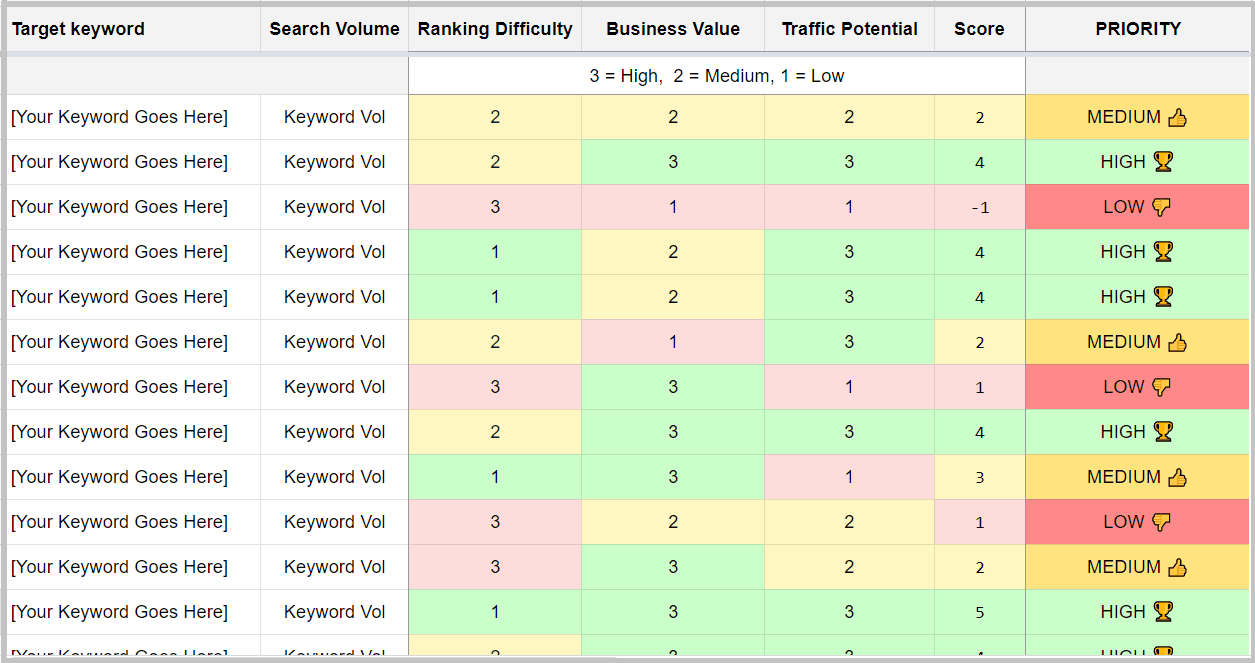
Make A Copy of The Google Sheet & Prioritize The Keyword List At Scale
Actionable Insights 🡭
When evaluating the ranking difficulty of a keyword, always look for the following:
1. Backlink profile – study the quality and quantity of backlinks to the top-ranking pages
2. Content depth of top pages – study the content structure, headings structure, or use tools like frase, thruuu, marketmuse (, etc.) to find the topics covered in their page.
3. Topical authority of the site in the topic
4. Search intent – can you satisfy the searcher’s intent?